Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Clinical Study
- Serum Transferrin Predicts New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Jong Dai Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, Keun-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):610-617. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.721
- 4,393 View
- 98 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
It is well known that high serum ferritin, a marker of iron storage, predicts incident type 2 diabetes. Limited information is available on the association between transferrin, another marker of iron metabolism, and type 2 diabetes. Thus, we investigated the association between transferrin and incident type 2 diabetes.
Methods
Total 31,717 participants (mean age, 40.4±7.2 years) in a health screening program in 2005 were assessed via cross-sectional analysis. We included 30,699 subjects who underwent medical check-up in 2005 and 2009 and did not have type 2 diabetes at baseline in this retrospective longitudinal analysis.
Results
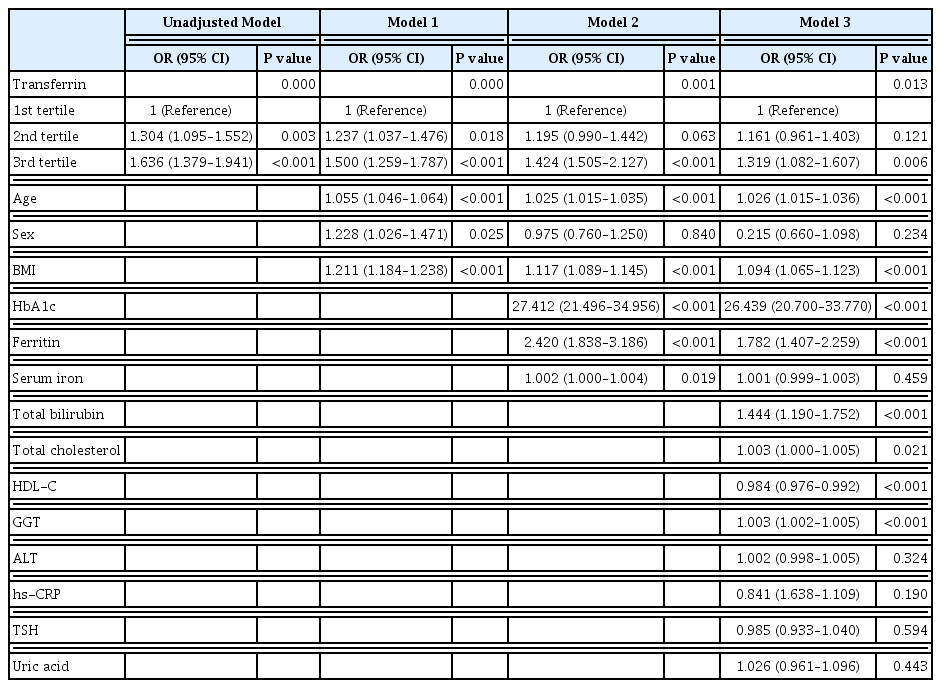
The serum transferrin level was higher in the type 2 diabetes group than in the non-type 2 diabetes group (58.32±7.74 μmol/L vs. 56.17±7.96 μmol/L, P<0.001). Transferrin correlated with fasting serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in the correlational analysis (r=0.062, P<0.001 and r=0.077, P<0.001, respectively) after full adjustment for covariates. Transferrin was more closely related to homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance than to homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (r=0.042, P<0.001 and r=–0.019, P=0.004, respectively) after full adjustment. Transferrin predicted incident type 2 diabetes in non-type 2 diabetic subjects in a multivariate linear regression analysis; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) of the 3rd tertile compared to that in the 1st tertile of transferrin for incident diabetes was 1.319 (95% CI, 1.082 to 1.607) after full adjustment (P=0.006).
Conclusion
Transferrin is positively associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes
Xingyue Wang, You Wang, Junjie Hou, Hongyang Liu, Rong Zeng, Xiangyu Li, Mei Han, Qingrun Li, Linong Ji, Desi Pan, Weiping Jia, Wen Zhong, Tao Xu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Proteomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer in Patients with Diabetes
Muhammad Mujammami, Mohamed Rafiullah, Khalid Akkour, Assim A. Alfadda, Afshan Masood, Salini Scaria Joy, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Eman Alshehri, Ibrahim O. Alanazi, Hicham Benabdelkamel
ACS Omega.2024; 9(4): 4721. CrossRef - Association between systemic iron status and β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Yao Qin, Yiting Huang, Yuxiao Li, Lu Qin, Qianying Wei, Xin Chen, Chuanhui Yang, Mei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Serum Level of Ceruloplasmin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Transferrin as Markers of Severity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Patricia-Andrada Reștea, Ștefan Țigan, Laura Grațiela Vicaș, Luminița Fritea, Eleonora Marian, Tunde Jurca, Annamaria Pallag, Iulius Liviu Mureșan, Corina Moisa, Otilia Micle, Mariana Eugenia Mureșan
Microbiology Research.2023; 14(4): 1670. CrossRef
- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



